Lithium Valley: A Modern Gold Rush
Share

California’s Lithium Valley: A Unique Resource at the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea in California has long been known for its geothermal power production, but in recent years, it has gained attention for another valuable resource: lithium. The area has been dubbed “Lithium Valley” and is home to over 2,000 lithium claims.
Lithium Recovery from Geothermal Brine: An Environmentally Responsible Method
Unlike traditional mining and extraction techniques used in other parts of the world, lithium is extracted from hot underground brine in a process that does not require hard rock mines or expansive evaporation ponds. Instead, a technology known as “ion exchange” or “molecular sieve” is used to separate lithium ions from other minerals in the solution. The lithium is then removed and purified, while the remaining brine is returned to the aquifer underground. The entire process takes place inside a secure tank and uses renewable geothermal power.
The Potential of Lithium Recovery at the Salton Sea: Near Zero CO2 Emissions and Renewable Energy
The potential of lithium recovery at the Salton Sea is significant. Although there are less than 300 parts per million (ppm) of lithium in the geothermal brine, it is estimated that the area could provide a 75-year supply that could supply up to a quarter of the world’s lithium market. Furthermore, the process has minimal environmental impact, as it produces near-zero CO2 emissions, uses renewable energy, and requires minimal water use.
The Three Main Players in Salton Sea’s Lithium Valley
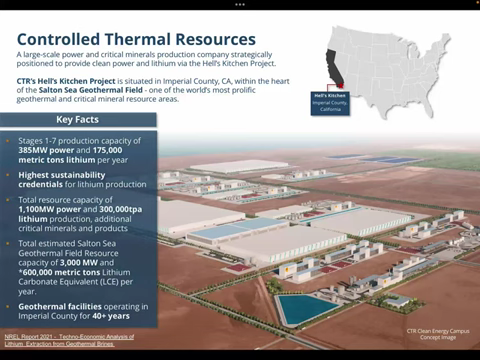
Currently, three main companies are leading the way in Salton Sea’s Lithium Valley: CalEnergy, Controlled Thermal Resources, and EnergySource Minerals. CalEnergy operates 10 of the 11 Salton Sea geothermal power plants, while Controlled Thermal Resources recently completed drilling for a future hybrid geothermal/lithium production plant. EnergySource Minerals, which operates the other geothermal power plant, has just received approval for its premier commercial-scale lithium project, ATLiS.
Advocating for Salton Sea Restoration Amid the White Gold Rush
Despite the potential benefits of lithium extraction, there are concerns about its impact on the Salton Sea ecosystem. Locals and residents living around the lake are advocating for a portion of the revenue generated from lithium extraction to go towards restoring the Salton Sea.
As the race to produce domestic supplies of lithium continues, the clock is ticking to determine if producing lithium at the Salton Sea is technically and commercially feasible in an environmentally sensitive way. Only time will tell if the “White Gold Rush” at the Salton Sea’s Lithium Valley will prove to be a valuable resource for both the energy and technology sectors, while also preserving the natural environment.
How will Lithium Extraction impact residents of salton sea area?

If lithium extraction at the Salton Sea becomes commercially viable, it could have significant impacts on the residents of the area. For one, it could potentially bring in jobs and revenue to the local economy. However, there are also concerns about the environmental impacts of lithium extraction and how it could affect the health and well-being of local residents.
The Salton Sea region is already facing numerous environmental and public health challenges, including high levels of air pollution and water contamination. There are concerns that lithium extraction could exacerbate these issues by depleting the already scarce water resources and contaminating the air and soil with potentially harmful chemicals used in the extraction process.
Additionally, there are concerns about the potential displacement of local communities if large-scale lithium extraction were to take place. It is important that the voices and concerns of local residents are heard and taken into consideration in any plans for lithium extraction at the Salton Sea.
Ultimately, the impact of lithium extraction on local residents will depend on the specific details of any proposed projects and how well they are able to mitigate potential environmental and public health risks. It is important that any such projects are carried out in a responsible and sustainable manner, with input and involvement from the local community.
How will Lithium Extraction negatively impact the environment
Negative impacts:
- Water depletion: The lithium extraction process requires significant amounts of water, and in a region already facing water scarcity, this could have serious consequences. Drawing water from the Salton Sea could also lead to further decline in its already shrinking water levels.
- Contamination: The process of extracting lithium from brine involves the use of chemicals and solvents that could potentially contaminate the surrounding air, soil, and water sources.
- Wildlife disruption: The Salton Sea is home to a variety of bird species, and the disturbance caused by lithium extraction could negatively impact their habitats and migration patterns.
how can Lithium Extraction positively impact the environment
Positive impacts:
- Renewable energy: The geothermal energy used to extract lithium is a clean, renewable energy source that could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Economic benefits: Lithium extraction could bring jobs and revenue to the local economy, which could in turn support the restoration and preservation of the Salton Sea ecosystem.
- Battery storage: Lithium is a key component in battery storage technology, which is essential for the transition to renewable energy sources. The availability of domestic lithium supplies could help drive down the costs of battery storage and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
In order to maximize the positive impacts and minimize the negative ones, it is essential that any lithium extraction projects are carried out in a responsible and sustainable manner. This includes using best practices to minimize water use and prevent contamination and ensuring that the concerns and voices of local communities and environmental advocates are taken into consideration.
What is lithium used for?
Lithium is a soft, silvery metal that is widely used in modern technology due to its unique chemical properties. It is a highly reactive element that has a low atomic weight and is capable of storing a large amount of energy in a small volume, making it an ideal material for batteries and other energy storage devices.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of rechargeable batteries used in a wide range of applications, from powering smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and energy storage systems for renewable energy sources. The high energy density of lithium-ion batteries allows them to store a large amount of energy in a small size, making them ideal for portable devices.
In addition to batteries, lithium is also used in a variety of other applications, including:
- Aerospace industry: Lithium is used to make lightweight alloys for aerospace applications, such as the manufacture of aircraft parts and satellites.
- Glass and ceramics: Lithium is used as a flux in the production of glass and ceramics, where it helps to reduce the melting temperature and improve the properties of the final product.
- Pharmaceuticals: Lithium is used as a mood stabilizer in the treatment of bipolar disorder and depression.
- Lubricants: Lithium is used as a thickener in high-performance lubricants, such as those used in the automotive industry.
Overall, lithium is a versatile and valuable material that is essential to modern technology and is expected to play an increasingly important role in the transition to renewable energy sources and the electrification of transportation.
Who is interested in pursuing Lithium Extraction in Salton Sea
There are several companies and organizations that are interested in pursuing lithium extraction at the Salton Sea. Some of the major players include:
- CalEnergy: This company operates 10 of the 11 geothermal power plants at the Salton Sea and is exploring the potential for lithium extraction.
- EnergySource Minerals: This company operates one of the geothermal power plants at the Salton Sea and has received approval for their premier commercial-scale lithium extraction project, Project ATLiS.
- Controlled Thermal Resources: This Australian company recently completed geothermal well drilling for the future Hell’s Kitchen hybrid geothermal/lithium production plant.
- Lithium Valley Commission: This organization was created by the California Energy Commission to explore the potential for lithium extraction at the Salton Sea and promote responsible and sustainable practices.
- Local communities: Residents of the Salton Sea area are interested in pursuing lithium extraction as a way to bring jobs and revenue to the local economy, but are also concerned about the potential impacts on the environment and the need for responsible and sustainable practices.
Overall, there is significant interest in exploring the potential for lithium extraction at the Salton Sea, but it is important to balance economic benefits with environmental responsibility and sustainability.
How can I invest in Lithium Extraction?
Investing in lithium extraction at the Salton Sea may be possible through investing in the companies that are involved in the project, such as CalEnergy, EnergySource Minerals, or Controlled Thermal Resources. However, it is important to note that investing in any company involves risk and requires careful consideration of factors such as financial performance, management, and market conditions.
Additionally, investing in lithium as a commodity can be done through various means, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, or stocks of companies that are involved in lithium production or exploration.
Before investing, it is important to do thorough research and consult with a financial advisor to determine if it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.